Physician Search
 |
 |
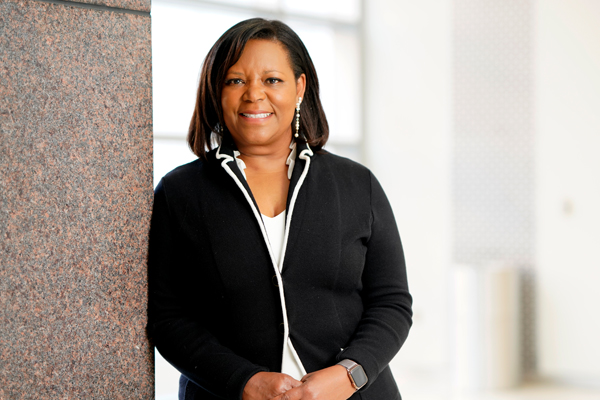
| Consuelo Wilkins, MD, MSCI, Senior Vice President for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) and Senior Associate Dean for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, always knew she wanted to be a physician. "Health equity was built into everything I did, even if I didn’t know it or recognize it at the time," Wilkins said. "I have always learned and believed that people are the same — everyone deserves to be healthy, and everyone should have the best opportunities to take care of themselves and their families." Click below to learn more about health equity initiatives. https://momentum.vicc.org/2021/09/everyone-deserves-to-be-healthy/ |
Vanderbilt was the lead site for an NIH-funded, phase 2, multicenter influenza vaccine study in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) recipients that may lead to a change in the current flu vaccine recommendations in this vulnerable population. Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH and colleagues recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, that two doses of high-dose trivalent flu vaccine resulted in higher amounts of influenza-specific antibodies than two doses of standard dose quadrivalent vaccine. https://news.vumc.org/2023/03/02/high-dose-flu-vaccine-beneficial-for-pediatric-stem-cell-transplant-patients/ |
Pembrolizumab versus Observation in Patients with Early Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer who had a Pathologic Complete Response after Chemotherapy plus Pembrolizumab, OptimICE-PCR Trial
Breast
Breast
This phase III trial compares the effect of continuation of treatment with pembrolizumab (usual approach) to observation only at preventing cancer from coming back in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) who achieved a pathologic complete response after preoperative chemotherapy in combination with pembrolizumab. The usual approach for patients with early-stage TNBC who receive preoperative chemotherapy plus pembrolizumab is to continue to receive pembrolizumab for up to 27 weeks after surgery. Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, such as pembrolizumab, may help the body's immune system attack the cancer, and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread. This trial may help researchers determine if observation is as good as receiving pembrolizumab for 27 weeks after surgery in triple-negative breast cancer patients who achieved a pathologic complete response after preoperative treatment with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab.
Breast
III
Abramson, Vandana
NCT05812807
VICC-NTBRE23357
Two Studies for Patients with Unfavorable Intermediate Risk Prostate Cancer Testing Less Intense Treatment for Patients with a Low Gene Risk Score and Testing a More Intense Treatment for Patients with a Higher Gene Risk Score, The Guidance Trial
Prostate
Prostate
This phase III trial uses the Decipher risk score to guide therapy selection. Decipher score is based on the activity of 22 genes in prostate tumor and may predict how likely it is for recurrent prostate cancer to spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Decipher score in this study is used for patient selection and the two variations of treatment to be studied: intensification for higher Decipher score or de-intensification for low Decipher score. Patients with higher Decipher risk score will be assigned to the part of the study that compares the use of 6 months of the usual treatment (hormone therapy and radiation treatment) to the use of darolutamide plus the usual treatment (intensification). The purpose of this section of the study is to determine whether the additional drug can reduce the chance of cancer coming back and spreading in patients with higher Decipher score. The addition of darolutamide to the usual treatment may better control the cancer and prevent it from spreading. Alternatively, patients with low Decipher risk score will be assigned to the part of the study that compares the use of radiation treatment alone (de-intensification) to the usual approach (6 months of hormone therapy plus radiation). The purpose of this part of the study is to determine if radiation treatment alone is as effective compared to the usual treatment without affecting the chance of tumor coming back in patients with low Decipher score prostate cancer. Radiation therapy uses high energy to kill tumor cells and reduce the tumor size. Hormone therapy drugs such as darolutamide suppress or block the production or action of male hormones that play role in prostate cancer development. Effect of radiation treatment alone in patients with low Decipher score prostate cancer could be the same as the usual approach in stabilizing prostate cancer and preventing it from spreading, while avoiding the side effects associated with hormonal therapy.
Prostate
III
Kirschner, Austin
NCT05050084
VICC-NTURO23322
Comparing an Alternative Surgical Procedure, Sentinel Lymph Node (SLN) Biopsy, with Standard Neck Dissection for Patients with Early-Stage Oral Cavity Cancer
Head/Neck
Head/Neck
This phase II/III trial studies how well sentinel lymph node biopsy works and compares sentinel lymph node biopsy surgery to standard neck dissection as part of the treatment for early-stage oral cavity cancer. Sentinel lymph node biopsy surgery is a procedure that removes a smaller number of lymph nodes from your neck because it uses an imaging agent to see which lymph nodes are most likely to have cancer. Standard neck dissection, such as elective neck dissection, removes many of the lymph nodes in your neck. Using sentinel lymph node biopsy surgery may work better in treating patients with early-stage oral cavity cancer compared to standard elective neck dissection.
Head/Neck
II/III
Topf, Michael
NCT04333537
NRGHN006
CRISPR-Edited Allogeneic Anti-CD19 CAR-T Cell Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory B Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (ANTLER)
Multiple Cancer Types
CB010A is a study evaluating safety, emerging efficacy, pharmacokinetics and immunogenicity
of CB-010 in adults with relapsed/refractory B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma after
lymphodepletion consisting of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine.
of CB-010 in adults with relapsed/refractory B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma after
lymphodepletion consisting of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine.
Lymphoma,
Phase I
I
Oluwole, Olalekan
NCT04637763
VICC-DTCTT23155P
Comparing the Outcome of Standard Systemic Therapy Only versus Standard Systemic therapy with either Surgery or Radiation Therapy, for Patients with Advanced Prostate cancer
Prostate
Prostate
This phase III trial compare the effects of adding definitive treatment (either radiation therapy or prostate removal surgery) to standard systemic therapy in treating patients with prostate cancer that has spread to other places in the body (advanced). Removing the prostate by either surgery or radiation therapy in addition to standard systemic therapy for prostate cancer may lower the chance of the cancer growing or spreading.
Prostate
III
Rini, Brian
NCT03678025
SWOGUROS1802
Testing the Addition of a New Drug, Daratumumab/rHuPH20, to the Usual Treatment (Lenalidomide) as Post-stem Cell Transplant Treatment for Multiple Myeloma, DRAMMATIC Study
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple Myeloma
This phase III trial compares the effect of usual treatment (lenalidomide) to using daratumumab/rHuPH20 plus the usual treatment after stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. This drug combination may help patients live longer after their stem cell transplant. Another purpose of this study is to learn if the presence and amount of minimal residual disease (MRD) can help doctors predict when a patients multiple myeloma will get worse. MRD is the name for the small number of cancer cells that remain in the patient even after their multiple myeloma has been treated and they have no symptoms of the disease. Drugs used in chemotherapy, such as lenalidomide, work in different ways to stop the growth of tumor cells, either by killing the cells, by stopping them from dividing, or by stopping them from spreading. Immunotherapy with daratumumab/rHuPH20, may induce changes in bodys immune system and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread. Giving lenalidomide and daratumumab/rHuPH20 may work better in treating patients with multiple myeloma compared to lenalidomide alone.
Multiple Myeloma
III
Baljevic, Muhamed
NCT04071457
VICC-NTPCL23369
Non-Chemotherapy Treatment (Ramucirumab plus Pembrolizumab) or Standard Chemotherapy for Treatment of Stage IV or Recurrent Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Following Immunotherapy, Pragmatica-Lung Trial
Lung
Lung
This phase III trial compares the effect of the combination therapy with ramucirumab and pembrolizumab versus standard of care chemotherapy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer that is stage IV or that has come back after a period of improvement (recurrent). Ramucirumab is a monoclonal antibody that may prevent the growth of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow. Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, such as pembrolizumab, may help the body's immune system attack the cancer, and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread. Chemotherapy drugs work in different ways to stop the growth of tumor cells, either by killing the cells, by stopping them from dividing, or by stopping them from spreading. This trial may help doctors find out if combination therapy with ramucirumab and pembrolizumab could help patients with stage IV or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer live longer compared to standard chemotherapy.
Lung
III
Iams, Wade
NCT05633602
VICC-NTTHO23073
Testing the Use of Steroids and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with Blinatumomab or Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed BCR-ABL-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults
Leukemia
Leukemia
This phase III trial compares the effect of usual treatment of chemotherapy and steroids and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) to the same treatment plus blinatumomab. Blinatumomab is a Bi-specific T-Cell Engager (BiTE) that may interfere with the ability of cancer cells to grow and spread. The information gained from this study may help researchers determine if combination therapy with steroids, TKIs, and blinatumomab work better than the standard of care.
Leukemia
III
Mohan, Sanjay
NCT04530565
ECOGHEMEA9181
Testing the Use of Investigational Drugs Atezolizumab and/or Bevacizumab with or without Standard Chemotherapy in the Second-Line Treatment of Advanced-Stage Head and Neck Cancers
This phase II/III compares the standard therapy (chemotherapy plus cetuximab) versus adding bevacizumab to standard chemotherapy, versus combination of just bevacizumab and atezolizumab in treating patients with head and neck cancer that has spread to other places in the body (metastatic or advanced stage) or has come back after prior treatment (recurrent). Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, such as atezolizumab, may help the body's immune system attack the cancer, and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread. Bevacizumab is in a class of medications called antiangiogenic agents. It works by stopping the formation of blood vessels that bring oxygen and nutrients to tumor. This may slow the growth and spread of tumor. Cetuximab is in a class of medications called monoclonal antibodies. It binds to a protein called EGFR, which is found on some types of cancer cells. This may help keep cancer cells from growing. Cisplatin and carboplatin are in a class of chemotherapy medications known as platinum-containing compounds. They work by killing, stopping, or slowing the growth of cancer cells. Docetaxel is in a class of chemotherapy medications called taxanes. It stops cancer cells from growing and dividing and may kill them. The addition of bevacizumab to standard chemotherapy or combination therapy with bevacizumab and atezolizumab may be better than standard chemotherapy plus cetuximab in treating patients with recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancers.
Not Available
II/III
Choe, Jennifer
NCT05063552
ECOGHNEA3202
A Study of a New Way to Treat Children and Young Adults with a Brain Tumor Called NGGCT
Multiple Cancer Types
This phase II trial studies the best approach to combine chemotherapy and radiation therapy (RT) based on the patients response to induction chemotherapy in patients with non-germinomatous germ cell tumors (NGGCT) that have not spread to other parts of the brain or body (localized). This study has 2 goals: 1) optimizing radiation for patients who respond well to induction chemotherapy to diminish spinal cord relapses, 2) utilizing higher dose chemotherapy followed by conventional RT in patients who did not respond to induction chemotherapy. Chemotherapy drugs, such as carboplatin, etoposide, ifosfamide, and thiotepa, work in different ways to stop the growth of tumor cells, either by killing the cells, by stopping them from dividing, or by stopping them from spreading. Radiation therapy uses high energy x-rays or high-energy protons to kill tumor cells and shrink tumors. Studies have shown that patients with newly-diagnosed localized NGGCT, whose disease responds well to chemotherapy before receiving radiation therapy, are more likely to be free of the disease for a longer time than are patients for whom the chemotherapy does not efficiently eliminate or reduce the size of the tumor. The purpose of this study is to see how well the tumors respond to induction chemotherapy to decide what treatment to give next. Some patients will be given RT to the spine and a portion of the brain. Others will be given high dose chemotherapy and a stem cell transplant before RT to the whole brain and spine. Giving treatment based on the response to induction chemotherapy may lower the side effects of radiation in some patients and adjust the therapy to a more efficient one for other patients with localized NGGCT.
Germ Cell (Pediatrics),
Pediatrics
II
Esbenshade, Adam
NCT04684368
COGACNS2021