Physician Search
 |
 |
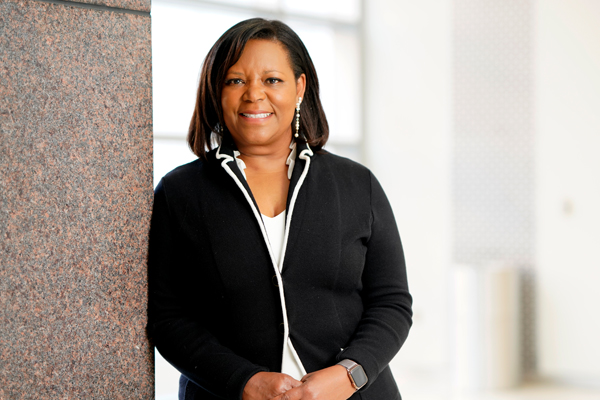
| Consuelo Wilkins, MD, MSCI, Senior Vice President for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) and Senior Associate Dean for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, always knew she wanted to be a physician. "Health equity was built into everything I did, even if I didn’t know it or recognize it at the time," Wilkins said. "I have always learned and believed that people are the same — everyone deserves to be healthy, and everyone should have the best opportunities to take care of themselves and their families." Click below to learn more about health equity initiatives. https://momentum.vicc.org/2021/09/everyone-deserves-to-be-healthy/ |
Vanderbilt was the lead site for an NIH-funded, phase 2, multicenter influenza vaccine study in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) recipients that may lead to a change in the current flu vaccine recommendations in this vulnerable population. Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH and colleagues recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, that two doses of high-dose trivalent flu vaccine resulted in higher amounts of influenza-specific antibodies than two doses of standard dose quadrivalent vaccine. https://news.vumc.org/2023/03/02/high-dose-flu-vaccine-beneficial-for-pediatric-stem-cell-transplant-patients/ |
Educational Telehealth Program for the Delivery of Care to Cancer Patients in Rural Communities, ENCORE Study
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
This clinical trial evaluates the clinical effectiveness of a multi-level telehealth-based intervention for cancer patients in rural communities. Rural residents face limited accessibility to cancer treatment and supportive care services, transportation barriers, and financial issues. Cancer Thriving and Surviving is an evidence-based self-management intervention with demonstrated efficacy across numerous chronic health conditions with dissemination across the US, inclusive of rural communities. This trial evaluates whether the evidence-based Cancer Thriving and Surviving intervention delivered through telehealth among rural patients may improve patient outcomes.
Miscellaneous
N/A
Friedman, Debra
NCT04758338
VICCPED2013
BXQ-350 Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Study in Cancer Patients
Supportive Care
Supportive Care
This study will assess pharmacokinetic (PK)/pharmacodynamic (PD) relationships and whether
BXQ-350 may decrease the intensity and/or duration of chemotherapy induced peripheral
neuropathy (CIPN) thereby improving quality of life (QoL) in cancer patients who have been
exposed to oxaliplatin and/or taxane-based chemotherapy. This study includes two randomized,
placebo controlled, blinded treatment cycles of BXQ-350/placebo, an optional open-label
BXQ-350 treatment period, and an unblinded Post-Treatment Follow-up period.
BXQ-350 may decrease the intensity and/or duration of chemotherapy induced peripheral
neuropathy (CIPN) thereby improving quality of life (QoL) in cancer patients who have been
exposed to oxaliplatin and/or taxane-based chemotherapy. This study includes two randomized,
placebo controlled, blinded treatment cycles of BXQ-350/placebo, an optional open-label
BXQ-350 treatment period, and an unblinded Post-Treatment Follow-up period.
Supportive Care
Early I
Agarwal, Rajiv
NCT05291286
VICC-DTSUP23096
A Study of ASTX030 (Cedazuridine in Combination With Azacitidine) in MDS, CMML, or AML
Multiple Cancer Types
Study ASTX030-01 is designed to move efficiently from Phase 1 to Phase 3. Phase 1 consists of
an open-label Dose Escalation Stage (Stage A) using multiple cohorts at escalating dose
levels of oral cedazuridine and azacitidine (only one study drug will be escalated at a time)
followed by a Dose Expansion Stage (Stage B) of ASTX030. Phase 2 is a randomized open-label
crossover study to compare oral ASTX030 to subcutaneous (SC) azacitidine. Phase 3 is a
randomized open-label crossover study comparing the final oral ASTX030 dose to SC
azacitidine. The duration of the study is expected to be approximately 48 months.
an open-label Dose Escalation Stage (Stage A) using multiple cohorts at escalating dose
levels of oral cedazuridine and azacitidine (only one study drug will be escalated at a time)
followed by a Dose Expansion Stage (Stage B) of ASTX030. Phase 2 is a randomized open-label
crossover study to compare oral ASTX030 to subcutaneous (SC) azacitidine. Phase 3 is a
randomized open-label crossover study comparing the final oral ASTX030 dose to SC
azacitidine. The duration of the study is expected to be approximately 48 months.
Leukemia,
Myelodysplastic Syndrome,
Phase I
I/II/III
Savona, Michael
NCT04256317
VICCHEMP19146
A Study of E7386 in Combination With Other Anticancer Drug in Participants With Solid Tumor
Multiple Cancer Types
The primary objective of this study is to assess the safety and tolerability and to determine
the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of E7386 in combination with other anticancer drug(s).
the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of E7386 in combination with other anticancer drug(s).
Gynecologic,
Liver,
Phase I
I
Heumann, Thatcher
NCT04008797
VICC-DTPHI23106
Niraparib and Dostarlimab as Neoadjuvant Treatment for Patients with BRCA-Mutated or PALB2-Mutated Stage I-III Breast Cancer
Breast
Breast
This phase II trial studies the effects of niraparib in combination with dostarlimab prior to surgery in treating BRCA-mutated or PALB2-mutated stage I-III breast cancer. Niraparib is a PARP inhibitor, which means that it blocks an enzyme (proteins that help chemical reactions in the body occur) in cells called PARP. PARP helps repair deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) when it becomes damaged. Blocking PARP may help keep cancer cells from repairing their damaged DNA, causing them to die. PARP inhibitors are a type of targeted therapy. Dostarlimab stimulates the immune system by blocking the PD-1 pathway. The PD-1 pathway controls the bodys natural immune response, but for some types of cancer, the immune system does not work as it should and is prevented from attacking tumors. Dostarlimab works by blocking the PD-1 pathway, which may help your immune system identify and catch tumor cells. Giving niraparib in combination with dostarlimab may work better against the tumor and maximize tumor shrinkage before surgery.
Breast
II
Abramson, Vandana
NCT04584255
VICCBRE2190
Ramucirumab and Trifluridine/Tipiracil or Paclitaxel for the Treatment of Patients with Previously Treated Advanced Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer
Gastric/Gastroesophageal
Gastric/Gastroesophageal
This phase II trial studies the effect of the combination of ramucirumab and trifluridine/tipiracil or paclitaxel in treating patients with previously treated gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer that has spread to other places in the body (advanced). Ramucirumab may damage tumor cells by targeting new blood vessel formation. Trifluridine/tipiracil is a chemotherapy pill and that may damage tumor cells by damaging their deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Paclitaxel may block cell growth by stopping cell division which may kill tumor cells. Giving ramucirumab and trifluridine/tipiracil will not be worse than ramucirumab and paclitaxel in treating gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer.
Gastric/Gastroesophageal
II
Gibson, Mike
NCT04660760
VICCGI2168
Avelumab with Binimetinib, Sacituzumab Govitecan, or Liposomal Doxorubicin in Treating Patients with Stage IV or Unresectable, Recurrent Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Breast
Breast
This phase II trial studies how well the combination of avelumab with liposomal doxorubicin with or without binimetinib, or the combination of avelumab with sacituzumab govitecan works in treating patients with triple negative breast cancer that is stage IV or is not able to be removed by surgery (unresectable) and has come back (recurrent). Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors like avelumab require activation of the patient's immune system. This trial includes a two week induction or lead-in of medications that can stimulate the immune system. It is our hope that this induction will improve the response to immunotherapy with avelumab. One treatment, sacituzumab govitecan, is a monoclonal antibody called sacituzumab linked to a chemotherapy drug called SN-38. Sacituzumab govitecan is a form of targeted therapy because it attaches to specific molecules (receptors) on the surface of tumor cells, known as TROP2 receptors, and delivers SN-38 to kill them. Another treatment, liposomal doxorubicin, is a form of the anticancer drug doxorubicin that is contained in very tiny, fat-like particles. It may have fewer side effects and work better than doxorubicin, and may enhance factors associated with immune response. The third medication is called binimetinib, which may stop the growth of tumor cells by blocking some of the enzymes needed for cell growth, and may help activate the immune system. It is not yet known whether giving avelumab in combination with liposomal doxorubicin with or without binimetinib, or the combination of avelumab with sacituzumab govitecan will work better in treating patients with triple negative breast cancer.
Breast
II
Abramson, Vandana
NCT03971409
VICCBRE1987
Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, and Optimal Dose of Candidate GBM Vaccine VBI-1901 in Recurrent GBM Subjects
Neuro-Oncology
Neuro-Oncology
The purpose of this study is to assess the safety and tolerability of VBI-1901 in subjects
with recurrent malignant gliomas (glioblastoma, or GBM).
with recurrent malignant gliomas (glioblastoma, or GBM).
Neuro-Oncology
I/II
Merrell, Ryan
NCT03382977
VICCNEUP2234
Ruxolitinib in Preventing Breast Cancer in Patients with High Risk and Precancerous Breast Lesions
Breast
Breast
This phase II trial studies how well ruxolitinib before surgery works in preventing breast cancer in patients with high risk and precancerous breast conditions. Ruxolitinib may changes the breast cell when administered to participants with precancerous breast conditions. Ruxolitinib may stop the growth of cells by blocking some of the enzymes needed for cell growth.
Breast
II
Meszoely, Ingrid
NCT02928978
VICCBRE1904
A Study of ASP3082 in Adults With Previously Treated Solid Tumors
Phase I
Phase I
Genes contain genetic code which tell the body which proteins to make. Many types of cancer
are caused by changes, or mutations, in a gene called KRAS. Researchers are looking for ways
to stop the actions of abnormal proteins made from the mutated KRAS gene. The so-called G12D
mutation in the KRAS gene is common in people with some solid tumors.
ASP3082 is a potential new treatment for certain solid tumors in people who have the G12D
mutation in their KRAS gene. Before ASP3082 is available as a treatment, the researchers need
to understand how it is processed by and acts upon the body. This information will help find
a suitable dose and to check for potential medical problems from the treatment.
People in this study will be adults with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic solid
tumors with the G12D mutation in their KRAS gene (G12D mutation). Locally advanced means the
cancer has spread to nearby tissue. Unresectable means the cancer cannot be removed by
surgery. Metastatic means the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. They will have
been previously treated with standard therapies or refused to receive those treatments. In
the European Union (EU) and South Korea, people who have refused to receive treatment with
standard therapies cannot take part.
The main aims of the study are: to check the safety of ASP3082 by itself and together with
cetuximab (a common cancer medicine), how well it is tolerated, and to find a suitable dose
of ASP3082 by itself and together with cetuximab.
This is an open-label study. This means that people in this study and clinic staff will know
that they will receive ASP3082.
This study will be in 2 parts. In Part 1, different small groups of people will receive lower
to higher doses of ASP3082, by itself, or together with cetuximab. Only people with
colorectal cancer will receive ASP3082 together with cetuximab. Any medical problems will be
recorded at each dose. This is done to find suitable doses of ASP3082 by itself or together
with cetuximab to use in Part 2 of the study. The first group will receive the lowest dose of
ASP3082. A medical expert panel will check the results from this group and decide if the next
group can receive a higher dose of ASP3082. The panel will do this for each group until all
groups have received ASP3082 (by itself or together with cetuximab) or until suitable doses
have been selected for Part 2.
In Part 2, other different small groups of people will receive ASP3082 by itself or together
with cetuximab, with the most suitable doses worked out from Part 1. This will help find a
more accurate dose of ASP3082 to use in future studies.
ASP3082, and cetuximab (if used), will be given through a vein. This is called an infusion.
Each treatment cycle is 21 days long. They will continue treatment until: they have medical
problems from the treatment they can't tolerate; their cancer gets worse; they start other
cancer treatment; they ask to stop treatment; they do not come back for treatment.
People will visit the clinic on certain days during their treatment, with extra visits during
the first 2 cycles of treatment. During these visits, the study doctors will check for any
medical problems from ASP3082 by itself or together with cetuximab. At some visits, other
checks will include a medical examination, echocardiogram (ECHO) or multigated acquisition
(MUGA) scan, blood and urine tests and vital signs. Vital signs include temperature, pulse,
breathing rate, and blood pressure. (Blood oxygen levels will also be checked for people
treated with ASP3082 together with cetuximab.) Tumor samples will be taken during certain
visits during treatment and when treatment has finished.
People will visit the clinic within 7 days after stopping treatment. The study doctors will
check for any medical problems from ASP3082 by itself or together with cetuximab. Other
checks will include a medical examination, echocardiogram (ECHO) or multigated acquisition
(MUGA) scan, urine and blood tests and vital signs. After this, people will continue to visit
the clinic every 9 weeks. This is to check the condition of their cancer. They will do this
until 45 weeks after treatment stopped, or if their cancer is worse, they start other cancer
treatment, they ask to stop treatment, or they do not come back for treatment.
Also, people may visit the clinic at 30 days and 90 days after stopping treatment. At the
30-day visit, the study doctors will check for any medical problems from ASP3082 by itself or
together with cetuximab. People will have their vital signs checked and have some bloo
are caused by changes, or mutations, in a gene called KRAS. Researchers are looking for ways
to stop the actions of abnormal proteins made from the mutated KRAS gene. The so-called G12D
mutation in the KRAS gene is common in people with some solid tumors.
ASP3082 is a potential new treatment for certain solid tumors in people who have the G12D
mutation in their KRAS gene. Before ASP3082 is available as a treatment, the researchers need
to understand how it is processed by and acts upon the body. This information will help find
a suitable dose and to check for potential medical problems from the treatment.
People in this study will be adults with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic solid
tumors with the G12D mutation in their KRAS gene (G12D mutation). Locally advanced means the
cancer has spread to nearby tissue. Unresectable means the cancer cannot be removed by
surgery. Metastatic means the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. They will have
been previously treated with standard therapies or refused to receive those treatments. In
the European Union (EU) and South Korea, people who have refused to receive treatment with
standard therapies cannot take part.
The main aims of the study are: to check the safety of ASP3082 by itself and together with
cetuximab (a common cancer medicine), how well it is tolerated, and to find a suitable dose
of ASP3082 by itself and together with cetuximab.
This is an open-label study. This means that people in this study and clinic staff will know
that they will receive ASP3082.
This study will be in 2 parts. In Part 1, different small groups of people will receive lower
to higher doses of ASP3082, by itself, or together with cetuximab. Only people with
colorectal cancer will receive ASP3082 together with cetuximab. Any medical problems will be
recorded at each dose. This is done to find suitable doses of ASP3082 by itself or together
with cetuximab to use in Part 2 of the study. The first group will receive the lowest dose of
ASP3082. A medical expert panel will check the results from this group and decide if the next
group can receive a higher dose of ASP3082. The panel will do this for each group until all
groups have received ASP3082 (by itself or together with cetuximab) or until suitable doses
have been selected for Part 2.
In Part 2, other different small groups of people will receive ASP3082 by itself or together
with cetuximab, with the most suitable doses worked out from Part 1. This will help find a
more accurate dose of ASP3082 to use in future studies.
ASP3082, and cetuximab (if used), will be given through a vein. This is called an infusion.
Each treatment cycle is 21 days long. They will continue treatment until: they have medical
problems from the treatment they can't tolerate; their cancer gets worse; they start other
cancer treatment; they ask to stop treatment; they do not come back for treatment.
People will visit the clinic on certain days during their treatment, with extra visits during
the first 2 cycles of treatment. During these visits, the study doctors will check for any
medical problems from ASP3082 by itself or together with cetuximab. At some visits, other
checks will include a medical examination, echocardiogram (ECHO) or multigated acquisition
(MUGA) scan, blood and urine tests and vital signs. Vital signs include temperature, pulse,
breathing rate, and blood pressure. (Blood oxygen levels will also be checked for people
treated with ASP3082 together with cetuximab.) Tumor samples will be taken during certain
visits during treatment and when treatment has finished.
People will visit the clinic within 7 days after stopping treatment. The study doctors will
check for any medical problems from ASP3082 by itself or together with cetuximab. Other
checks will include a medical examination, echocardiogram (ECHO) or multigated acquisition
(MUGA) scan, urine and blood tests and vital signs. After this, people will continue to visit
the clinic every 9 weeks. This is to check the condition of their cancer. They will do this
until 45 weeks after treatment stopped, or if their cancer is worse, they start other cancer
treatment, they ask to stop treatment, or they do not come back for treatment.
Also, people may visit the clinic at 30 days and 90 days after stopping treatment. At the
30-day visit, the study doctors will check for any medical problems from ASP3082 by itself or
together with cetuximab. People will have their vital signs checked and have some bloo
Phase I
I
Berlin, Jordan
NCT05382559
VICCPHI2207