Physician Search
 |
 |
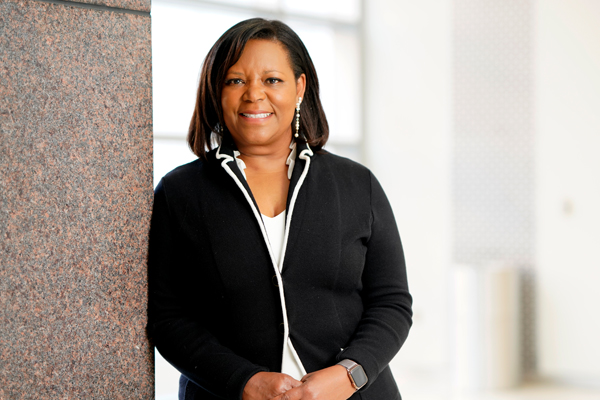
| Consuelo Wilkins, MD, MSCI, Senior Vice President for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) and Senior Associate Dean for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, always knew she wanted to be a physician. "Health equity was built into everything I did, even if I didn’t know it or recognize it at the time," Wilkins said. "I have always learned and believed that people are the same — everyone deserves to be healthy, and everyone should have the best opportunities to take care of themselves and their families." Click below to learn more about health equity initiatives. https://momentum.vicc.org/2021/09/everyone-deserves-to-be-healthy/ |
Vanderbilt was the lead site for an NIH-funded, phase 2, multicenter influenza vaccine study in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) recipients that may lead to a change in the current flu vaccine recommendations in this vulnerable population. Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH and colleagues recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, that two doses of high-dose trivalent flu vaccine resulted in higher amounts of influenza-specific antibodies than two doses of standard dose quadrivalent vaccine. https://news.vumc.org/2023/03/02/high-dose-flu-vaccine-beneficial-for-pediatric-stem-cell-transplant-patients/ |
Testing Lutetium Lu 177 Dotatate in Patients with Somatostatin Receptor Positive Advanced Bronchial Neuroendocrine Tumors
Lung
Lung
This phase II trial studies the effect of lutetium Lu 177 dotatate compared to the usual treatment (everolimus) in treating patients with somatostatin receptor positive bronchial neuroendocrine tumors that have spread to other places in the body (advanced). Radioactive drugs, such as lutetium Lu 177 dotatate, may carry radiation directly to tumor cells and may reduce harm to normal cells. Lutetium Lu 177 dotatate may be more effective than everolimus in shrinking or stabilizing advanced bronchial neuroendocrine tumors.
Lung
II
Ramirez, Robert
NCT04665739
SWOGTHOA021901
A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Tolerability of TOS-358 in Adults With Select Solid Tumors
Multiple Cancer Types
The goal of this clinical trial is to evaluate the safety of TOS-358 in adults with select
solid tumors who meet study enrollment criteria. The main questions it aims to answer are:
1. what is the maximum tolerated dose and recommended dose for phase 2?
2. how safe and tolerable is TOS-358 at different dose levels when taken orally once or
twice per day?
solid tumors who meet study enrollment criteria. The main questions it aims to answer are:
1. what is the maximum tolerated dose and recommended dose for phase 2?
2. how safe and tolerable is TOS-358 at different dose levels when taken orally once or
twice per day?
Breast,
Cervical,
Gastrointestinal,
Gynecologic,
Head/Neck,
Lung,
Phase I,
Urologic
I
Berlin, Jordan
NCT05683418
VICC-DTPHI23103
A Study of E7386 in Combination With Other Anticancer Drug in Participants With Solid Tumor
Multiple Cancer Types
The primary objective of this study is to assess the safety and tolerability and to determine
the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of E7386 in combination with other anticancer drug(s).
the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of E7386 in combination with other anticancer drug(s).
Gynecologic,
Liver,
Phase I
I
Heumann, Thatcher
NCT04008797
VICC-DTPHI23106
A Study Evaluating an Advanced Pneumatic Compression Device Versus Usual Care for Treatment of Head and Neck Lymphedema
Head/Neck
Head/Neck
To compare the effectiveness of an APCD to Usual Care in the management of lymphedema and
fibrosis (LEF) in head and neck cancer (HNC) survivors.
fibrosis (LEF) in head and neck cancer (HNC) survivors.
Head/Neck
N/A
Murphy, Barbara
NCT04797390
VICCHN2111
Dose Optimization and Expansion Study of DFV890 in Adult Patients With Myeloid Diseases
Hematologic
Hematologic
Study CDFV890G12101 is an open-label, phase 1b, multicenter study with a randomized two-dose
optimization part, and a dose expansion part consisting of two groups evaluating DFV890 in
patients with myeloid diseases. The purpose of this study is to assess the safety,
tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, efficacy and recommended dose for single
agent DFV890 in patients with lower risk (LR: very low, low or intermediate risk)
myelodysplastic syndromes (LR MDS) and lower risk chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (LR CMML).
optimization part, and a dose expansion part consisting of two groups evaluating DFV890 in
patients with myeloid diseases. The purpose of this study is to assess the safety,
tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, efficacy and recommended dose for single
agent DFV890 in patients with lower risk (LR: very low, low or intermediate risk)
myelodysplastic syndromes (LR MDS) and lower risk chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (LR CMML).
Hematologic
I
Kishtagari, Ashwin
NCT05552469
VICC-DTHEM23007P
Acalabrutinib for the Treatment of Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
This phase II trial studies how well acalabrutinib works in treating patients with chronic graft versus host disease. Acalabrutinib may be an effective treatment for graft-versus-host disease caused by a stem cell transplant.
Miscellaneous
II
Kitko, Carrie
NCT04198922
VICCCTT2122
A Phase 1 Study of AB521 in Renal Cell Carcinoma and Other Solid Tumors
Multiple Cancer Types
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the safety and tolerability of AB521 when taken
alone in participants with advanced solid tumor malignancies and clear cell renal cell
carcinoma (ccRCC).
alone in participants with advanced solid tumor malignancies and clear cell renal cell
carcinoma (ccRCC).
Kidney (Renal Cell),
Phase I
I
Rini, Brian
NCT05536141
VICC-DTURO23168P
Avelumab or Hydroxychloroquine with or without Palbociclib for the Treatment of Stage II-III Breast Cancer, PALAVY Study
Breast
Breast
This phase II trial investigates the effect of avelumab or hydroxychloroquine sulfate with or without palbociclib in treating patients with stage II-III breast cancer that is positive for disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) after curative therapy. DTCs are breast cancer cells that are asleep (dormant) in the bone marrow. There are multiple ways in which these cells stay alive, and three of these mechanisms are inhibited by the drugs in this trial. First, dormant cancer cells need a protein signal pathway involving CDK 4/6 to start dividing once they wake up in order to survive as an active cancer cell. Palbociclib works by blocking the CDK 4/6 protein and by doing so may limit the dormant cancer cell from being able to survive. In addition, palbociclib may also help both of the other drugs in the trial to work better. Second, dormant cancer cells also use a process called autophagy to generate their own nutrition, which can allow them to stay asleep. Hydroxychloroquine has been shown to block autophagy, which leads to starvation of the cells. Third, dormant cancer cells are able to hide from the bodys immune system. The immune system sends a type of cell called T cells throughout the body to detect and fight infections and diseasesincluding cancers. One way the immune system controls the activity of T cells is through the PD-1/PD-L1 (programmed cell death protein-1) pathway. However, some cancer cells hide from T-cell attack by taking control of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction and this stops T cells from attacking cancer cells. Avelumab is an antibody designed to block the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and helps the immune system in detecting and fighting dormant cancer cells. Because palbociclib, hydroxychloroquine, and avelumab work on the mechanisms that keep the dormant cells alive, taking one or a combination of these drugs may be able to eliminate DTCs.
Breast
II
Reid, Sonya
NCT04841148
VICCBRE2161
Comparison of Chemotherapy before and after Surgery versus after Surgery Alone for the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer, OPT-IN Trial
Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal
This phase II/III trial compares the effect of adding chemotherapy before and after surgery versus after surgery alone (usual treatment) in treating patients with stage II-III gallbladder cancer. Chemotherapy drugs, such as gemcitabine and cisplatin, work in different ways to stop the growth of tumor cells, either by killing the cells, by stopping them from dividing, or by stopping them from spreading. Giving chemotherapy before surgery may make the tumor smaller; therefore, may reduce the extent of surgery. Additionally, it may make it easier for the surgeon to distinguish between normal and cancerous tissue. Giving chemotherapy after surgery may kill any remaining tumor cells. This study will determine whether giving chemotherapy before surgery increases the length of time before the cancer may return and whether it will increase a patients life span compared to the usual approach.
Gastrointestinal
II/III
Goff, Laura
NCT04559139
ECOGGIEA2197
Testing the Addition of Pembrolizumab, an Immunotherapy Cancer Drug to Olaparib Alone as Therapy for Patients with Pancreatic Cancer That Has Spread with Inherited BRCA Mutations
Pancreatic
Pancreatic
This phase II trial studies whether adding pembrolizumab to olaparib (standard of care) works better than olaparib alone in treating patients with pancreatic cancer with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations that has spread to other places in the body (metastatic). BRCA1 and BRCA2 are human genes that produce tumor suppressor proteins. These proteins help repair damaged deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and, therefore, play a role in ensuring the stability of each cells genetic material. When either of these genes is mutated, or altered, such that its protein product is not made or does not function correctly, DNA damage may not be repaired properly. As a result, cells are more likely to develop additional genetic alterations that can lead to some types of cancer, including pancreatic cancer. Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, such as pembrolizumab, may help the body's immune system attack the cancer, and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread. Olaparib is an inhibitor of PARP, a protein that helps repair damaged DNA. Blocking PARP may help keep tumor cells from repairing their damaged DNA, causing them to die. PARP inhibitors are a type of targeted therapy. The addition of pembrolizumab to the usual treatment of olaparib may help to shrink tumors in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations.
Pancreatic
II
Cardin, Dana
NCT04548752
SWOGGIS2001