Physician Search
 |
 |
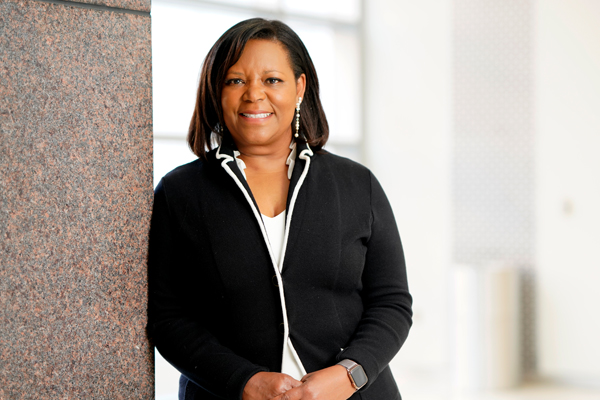
| Consuelo Wilkins, MD, MSCI, Senior Vice President for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) and Senior Associate Dean for Health Equity and Inclusive Excellence for Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, always knew she wanted to be a physician. "Health equity was built into everything I did, even if I didn’t know it or recognize it at the time," Wilkins said. "I have always learned and believed that people are the same — everyone deserves to be healthy, and everyone should have the best opportunities to take care of themselves and their families." Click below to learn more about health equity initiatives. https://momentum.vicc.org/2021/09/everyone-deserves-to-be-healthy/ |
Vanderbilt was the lead site for an NIH-funded, phase 2, multicenter influenza vaccine study in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) recipients that may lead to a change in the current flu vaccine recommendations in this vulnerable population. Natasha Halasa, MD, MPH and colleagues recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, that two doses of high-dose trivalent flu vaccine resulted in higher amounts of influenza-specific antibodies than two doses of standard dose quadrivalent vaccine. https://news.vumc.org/2023/03/02/high-dose-flu-vaccine-beneficial-for-pediatric-stem-cell-transplant-patients/ |
pB1-11 and TA-HPV Vaccines Combined with Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Recurrent or Metastatic PD-L1 and HPV Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer
Head/Neck
Head/Neck
This phase II trial tests how well pB1-11 and human papillomavirus tumor antigen (TA-HPV) vaccines in combination with pembrolizumab work in treating patients with oropharyngeal cancer that has come back (recurrent) or that has spread from where it first started (primary site) to other places in the body (metastatic) and that is PD-L1 and human papillomavirus (HPV) positive. Oropharyngeal cancer is a type of head and neck cancer involving structures in the back of the throat (the oropharynx), such as the non-bony back roof of the mouth (soft palate), sides and back wall of the throat, tonsils, and back third of the tongue. Scientists have found that some strains or types of a virus called HPV can cause oropharyngeal cancer. pBI-11 is a circular deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (plasmid) vaccine that promotes antibody, cytotoxic T cell, and protective immune responses. TA-HPV is an investigational recombinant vaccina virus derived from a strain of the vaccina virus which was widely used for smallpox vaccination. Vaccination with this TA-HPV vaccine may stimulate the immune system to mount a cytotoxic T cell response against tumor cells positive for HPV, resulting in decreased tumor growth. Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, such as pembrolizumab, may help the body's immune system attack the cancer, and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread by inhibiting the PD-1 receptor. These investigational vaccines could cause or enhance an immune response in the body against HPV, during which time the activity of pembrolizumab against oropharyngeal cancer associated with HPV may be strengthened. These drugs in combination may be more effective in increasing the ability of the immune system to fight oropharyngeal cancer than pembrolizumab alone.
Head/Neck
II
Gibson, Mike
NCT05799144
VICCHN2208
Decitabine and Cedazuridine in Combination with Venetoclax for the Treatment of Patients who have Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia after Donor Stem Cell Transplant
Leukemia
Leukemia
This phase II trial tests how well decitabine and cedazuridine (DEC-C) works in combination with venetoclax in treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in patients whose AML has come back after a period of improvement (relapse) after a donor stem cell transplant. Cedazuridine is in a class of medications called cytidine deaminase inhibitors. It prevents the breakdown of decitabine, making it more available in the body so that decitabine will have a greater effect. Decitabine is in a class of medications called hypomethylation agents. It works by helping the bone marrow produce normal blood cells and by killing abnormal cells in the bone marrow. Venetoclax is in a class of medications called B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) inhibitors. It may stop the growth of cancer cells by blocking Bcl-2, a protein needed for cancer cell survival. Giving DEC-C in combination with venetoclax may kill more cancer cells in patients with relapsed AML.
Leukemia
II
Mohan, Sanjay
NCT05799079
VICCHEM2163
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy followed by Surgery for the Treatment of Soft Tissue Sarcomas
Sarcoma
Sarcoma
This phase II trial studies the effect of hypofractionated radiotherapy followed by surgery in treating patients with soft tissue sarcoma. Hypofractionated radiation therapy delivers higher doses of radiation therapy over a shorter period of time and may kill more tumor cells and have fewer side effects. Giving hypofractionated radiotherapy followed by surgery may allow patients with sarcomas to be treated in a much more rapid and convenient fashion.
Sarcoma
II
Shinohara, Eric
NCT04506008
VICCSAR2062
Total Body Irradiation and Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy with Atezolizumab and Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer, TESSERACT Trial
Multiple Cancer Types
This phase I/II trial studies the side effects, safety, and effectiveness of low dose radiation to the entire body (total body irradiation [TBI]) and higher dose radiation to known areas of cancer (hypofractionated radiation therapy [H-RT]) combined with atezolizumab and chemotherapy (carboplatin & etoposide) in treating patients with small cell lung cancer that has spread to disease sites outside of the lung (extensive stage). Extensive stage disease has historically been treated with chemotherapy alone with consideration of chest (thoracic) radiation therapy for those with response to chemotherapy, as well as consideration of preventative radiation therapy to the head (prophylactic cranial irradiation). Emerging evidence supports the synergistic interactions between immunotherapy and radiation therapy. Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, such as atezolizumab, may help the body's immune system attack the cancer, and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread. Carboplatin is in a class of medications known as platinum-containing compounds. It works in a way similar to the anticancer drug cisplatin, but may be better tolerated than cisplatin. Carboplatin works by killing, stopping or slowing the growth of tumor cells. Etoposide is in a class of medications known as podophyllotoxin derivatives. It blocks a certain enzyme needed for cell division and DNA repair and may kill tumor cells. Combining TBI and H-RT with atezolizumab and chemotherapy may improve response to treatment.
Lung,
Small Cell
I/II
Osmundson, Evan
NCT06110572
VICCTHOP2206
Gabapentin plus Ketamine for the Prevention of Acute and Chronic Pain in Patients with Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Undergoing Chemoradiation
Multiple Cancer Types
This phase I/II trial studies the side effects and best dose of a combination of gabapentin and ketamine and to see how well it works to prevent acute and chronic pain in patients receiving chemotherapy and radiation therapy (chemoradiation) for head and neck cancer that has spread to nearby tissue or lymph nodes (locally advanced). Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used to treat nerve related pain. Specifically, it has been used to treat pain involving the mouth, throat and nasal passages in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiation. Ketamine is a type of general anesthetic that blocks pathways to the brain involved with sensing pain. This trial may help doctors determine how patients tolerate the combination of gabapentin and ketamine and to find the correct dosing for ketamine in those taking gabapentin. This will be the basis for a future, larger study to look at how effective this combination is at reducing and/or preventing pain in head and neck cancer patients.
Head/Neck,
Phase I
I/II
Lockney, Natalie
NCT05156060
VICCHNP2173
Active Myeloid Target Compound Decitabine and Cedazuridine in Combination with Itacitinib for the Treatment of Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm (MDS/MPN) Overlap Syndromes, ABNL-MARRO Study
Multiple Cancer Types
This phase I/II trial tests the safety, side effects, and best dose of decitabine and cedazuridine (ASTX727) in combination with itacitinib and how well they work in treating patients with myelodysplastic/ myeloproliferative neoplasm. Cedazuridine is in a class of medications called cytidine deaminase inhibitors. It prevents the breakdown of decitabine, making it more available in the body so that decitabine will have a greater effect. Decitabine is in a class of medications called hypomethylation agents. It works by helping the bone marrow produce normal blood cells and by killing abnormal cells in the bone marrow. Itacitinib may stop the growth of cancer cells by blocking some of the enzymes needed for cell growth. Giving decitabine and cedazuridine in combination with itacitinib may work better in treating patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm.
Hematologic,
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
I/II
Savona, Michael
NCT04061421
VICCHEMP1977
Surgical Debulking Prior to Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Patients with Well Differentiated Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Multiple Cancer Types
This phase IV trial evaluates how well giving standard of care (SOC) peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) after SOC surgical removal of as much tumor as possible (debulking surgery) works in treating patients with grade 1 or 2, somatostatin receptor (SSTR) positive, gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs) that have spread from where they first started (primary site) to the liver (hepatic metastasis). Lutetium Lu 177 dotatate is a radioactive drug that uses targeted radiation to kill tumor cells. Lutetium Lu 177 dotatate includes a radioactive form (an isotope) of the element called lutetium. This radioactive isotope (Lu-177) is attached to a molecule called dotatate. On the surface of GEP-NET tumor cells, a receptor called a somatostatin receptor binds to dotatate. When this binding occurs, the lutetium Lu 177 dotatate drug then enters somatostatin receptor-positive tumor cells, and radiation emitted by Lu-177 helps kill the cells. Giving lutetium Lu 177 dotatate after surgical debulking may better treat patients with grade 1/2 GEP-NETs.
Colon,
Esophageal,
Gastric/Gastroesophageal,
Gastrointestinal,
Liver,
Pancreatic,
Rectal
IV
Idrees, Kamran
NCT06016855
VICCGI2283
A Study to Compare Treatment with the Drug Selumetinib Alone versus Selumetinib and Vinblastine in Patients with Recurrent or Progressive Low-Grade Glioma
This phase III trial investigates the best dose of vinblastine in combination with selumetinib and the benefit of adding vinblastine to selumetinib compared to selumetinib alone in treating children and young adults with low-grade glioma (a common type of brain cancer) that has come back after prior treatment (recurrent) or does not respond to therapy (progressive). Selumetinib is a drug that works by blocking a protein that lets tumor cells grow without stopping. Vinblastine blocks cell growth by stopping cell division and may kill cancer cells. Giving selumetinib in combination with vinblastine may work better than selumetinib alone in treating recurrent or progressive low-grade glioma.
Not Available
III
Esbenshade, Adam
NCT04576117
COGACNS1931
Pembrolizumab after Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy in Treating Patients with Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Lung
Lung
This phase II trial studies how well pembrolizumab after standard treatment with radiation plus the following chemotherapy drugs: cisplatin or carboplatin, plus etoposide works in treating patients with limited stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC). Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, such as pembrolizumab, may help the body's immune system attack the cancer, and may interfere with the ability of tumor cells to grow and spread. Giving pembrolizumab after standard treatment with radiation plus chemotherapy may increase the ability of the immune system to fight LS-SCLC.
Lung
II
Whitaker, Ryan
NCT06140407
VICCTHO22114
111In-Panitumumab for Nodal Staging in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Multiple Cancer Types
This phase I trial tests the safety and effectiveness of indium In 111 panitumumab (111In-panitumumab) for identifying the first lymph nodes to which cancer has spread from the primary tumor (sentinel lymph nodes) in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) undergoing surgery. The most important factor for survival for many cancer types is the presence of cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes (metastasis). Lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck cancer reduce the 5-year survival by half. Sometimes, the disease is too small to be found on clinical and imaging exams before surgery. 111In-panitumumab is in a class of medications called radioimmunoconjugates. It is composed of a radioactive substance (indium In 111) linked to a monoclonal antibody (panitumumab). Panitumumab binds to EGFR receptors, a receptor that is over-expressed on the surface of many tumor cells and plays a role in tumor cell growth. Once 111In-panitumumab binds to tumor cells, it is able to be seen using an imaging technique called single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT). SPECT/CT can be used to make detailed pictures of the inside of the body and to visualize areas where the radioactive drug has been taken up by the cells. Using 111In-panitumumab with SPECT/CT imaging may improve identification of sentinel lymph nodes in patients with head and neck squamous cell cancer undergoing surgery.
Head/Neck,
Phase I
I
Rosenthal, Eben
NCT05901545
VICC-EDHAN23201P